Prostate Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
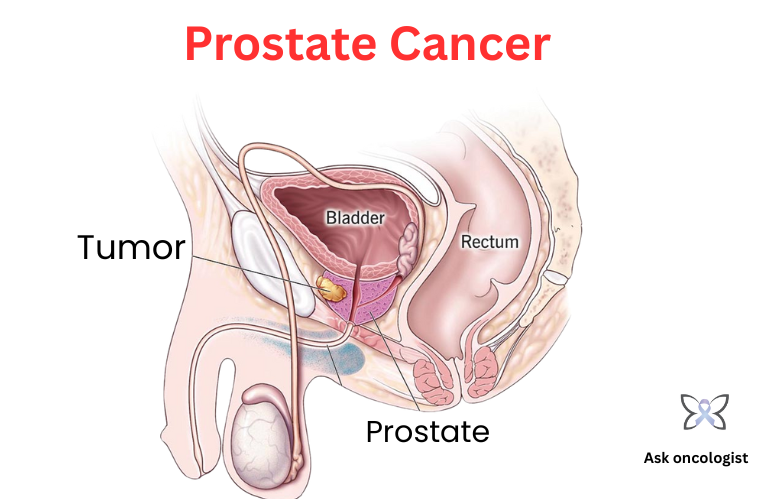
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer affecting men worldwide. It develops in the prostate gland, a small walnut-shaped organ that produces seminal fluid. While some prostate cancers grow slowly and may not cause significant harm, others can be aggressive and spread rapidly. Early detection and timely treatment can significantly improve outcomes. This article provides an in-depth look at prostate cancer, its symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures. If you're in need of expert guidance, consulting the best oncologist in Kakinada or the best cancer specialist in Kakinada can ensure you receive the most appropriate care.
Understanding Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer begins when abnormal cells in the prostate gland start to grow uncontrollably. It is classified into different stages based on the extent of its spread:
- Localized Prostate Cancer: Cancer is confined to the prostate gland.
- Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer: Cancer has spread beyond the prostate to nearby tissues.
- Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Cancer has spread to distant organs, such as the bones or lymph nodes.
There are different types of prostate cancer, with the most common being prostatic adenocarcinoma. Other rare forms include small cell carcinoma, neuroendocrine tumors, transitional cell carcinoma, and sarcomas.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing prostate cancer, including:
- Age: The risk increases significantly after the age of 50. Most cases are diagnosed in men over 65.
- Family History: A family history of prostate cancer, particularly in a father or brother, can elevate the risk.
- Genetics: Mutations in genes such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 may play a role in hereditary prostate cancer.
- Diet: Diets high in red meat, processed foods, and high-fat dairy products have been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer.
- Obesity: Excess weight can contribute to more aggressive forms of the disease, making early detection and treatment even more crucial.
- Hormonal Changes: High levels of male hormones, particularly testosterone, may influence prostate cancer growth.
- Inflammation of the Prostate (Prostatitis): Chronic inflammation may contribute to an increased risk of developing cancerous cells.
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
In its early stages, prostate cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms. However, as it progresses, symptoms may include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Blood in urine or semen
- Erectile dysfunction
- Discomfort in the pelvic area
- Pain in the bones (in advanced cases)
- Unexplained weight loss and fatigue
Many of these symptoms can also be linked to non-cancerous conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostatitis. Therefore, if you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to consult with the best prostate cancer doctor near me for proper diagnosis and care.
Diagnosis
Early detection is key to effective treatment. Doctors use several diagnostic tools to detect prostate cancer:
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: Measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate, in the blood. Elevated levels may indicate prostate cancer, though non-cancerous conditions can also cause increases. PSA testing is widely available, so you can look up PSA testing near me to find convenient locations for regular check-ups.
- Digital Rectal Examination (DRE): A physical examination where a doctor feels the prostate for abnormalities such as lumps or irregularities.
- Biopsy: A small tissue sample is taken from the prostate and analyzed for cancer cells. It is typically performed if PSA levels are elevated or if the DRE is abnormal.
- MRI and Ultrasound: Imaging techniques help in assessing the extent of the disease. Multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) provides a detailed look at prostate abnormalities.
- Bone Scans and CT Scans: Used to determine if cancer has spread beyond the prostate.
Prostate Cancer Staging
Once diagnosed, prostate cancer is staged to determine its severity:
- Stage I: Cancer is small and confined to the prostate.
- Stage II: Cancer remains within the prostate but is more significant in size.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread beyond the prostate to nearby tissues.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs such as bones, lymph nodes, or other parts of the body.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. Here are some of the latest treatment options available:
1. Active Surveillance
Recommended for slow-growing prostate cancer that does not cause symptoms. Regular monitoring is done through PSA tests and biopsies. This option is often chosen for older men or those with other serious health conditions.
2. Surgery (Radical Prostatectomy)
Involves the removal of the prostate gland and surrounding tissues. It is most effective for localized prostate cancer. Robotic-assisted surgery offers precision with minimal side effects. If you are considering prostate removal surgery, it’s important to consult with the best prostate doctor for personalized advice.
3. Radiation Therapy
Uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): Directs radiation from outside the body to the prostate.
- Brachytherapy: Involves placing radioactive seeds inside the prostate to deliver targeted radiation.
4. Hormone Therapy
Reduces the levels of male hormones (androgens) that promote cancer growth. This is often used for advanced cases. Methods include:
- Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonists
- Anti-androgens
- Orchiectomy (surgical removal of the testicles)
5. Chemotherapy
Utilized in cases where cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Common drugs include docetaxel and cabazitaxel.
6. Immunotherapy
Helps the body’s immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. Sipuleucel-T (Provenge) is a vaccine-based therapy for advanced prostate cancer.
7. Targeted Therapy
Focuses on specific genetic changes in cancer cells to halt their growth. PARP inhibitors, such as olaparib and rucaparib, are used in certain cases.
Latest Prostate Cancer Treatments
The field of prostate cancer treatment is continuously evolving. Researchers are working on new prostate cancer treatments that are 100% effective for various stages of the disease. Advances in personalized medicine are enabling doctors to tailor treatments based on individual genetic profiles, improving the chances of successful outcomes.
Lifestyle and Prevention
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent prostate cancer, certain lifestyle modifications can help lower the risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while reducing red meat and high-fat foods.
- Exercise Regularly: Staying active helps in maintaining a healthy weight and reducing cancer risk.
- Regular Screenings: Men over 50, or those with a family history, should undergo regular prostate check-ups.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption: Both can contribute to overall health deterioration.
- Manage Stress: Stress-reducing activities like meditation and yoga can improve overall well-being.
Living with Prostate Cancer
A prostate cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. Support groups and counseling can provide emotional assistance. Patients should also discuss treatment side effects, such as urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, and fatigue, with their doctors to manage quality of life effectively.
If you are concerned about prostate problems, whether benign or cancerous, it's important to seek medical advice early. The best prostate doctor will provide guidance, early detection, and treatment options to ensure the best possible outcome.
Conclusion
Prostate cancer is a serious but treatable disease if detected early. Regular screenings, a healthy lifestyle, and awareness of symptoms can help in early diagnosis and effective treatment. If you experience any unusual symptoms or have concerns about prostate cancer surgery, psa testing, or the latest prostate cancer treatments, consult a healthcare professional or seek out the best prostate cancer doctor near me. Regular screenings, such as PSA testing, can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment. With advancements in medicine, the outcomes for prostate cancer patients are better than ever.
Understanding prostate cancer is the first step toward prevention and treatment, leading to better health outcomes and an improved quality of life.