Understanding Oral (Mouth) Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment & Aftercare By Dr. K. Pradeep Bhaskar – Ask Oncologist, Kakinada
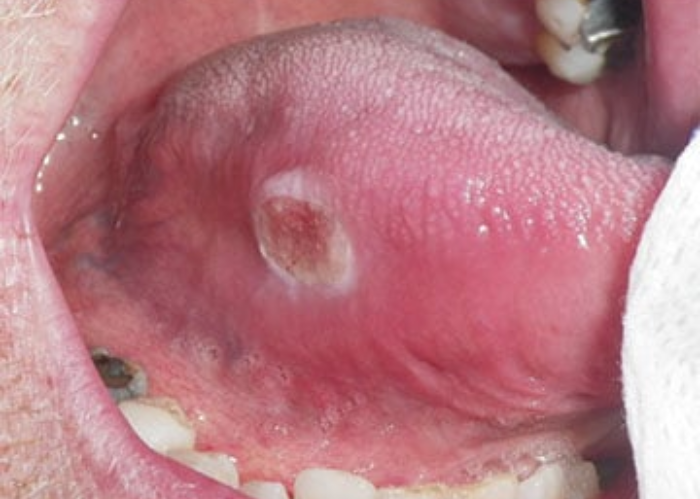
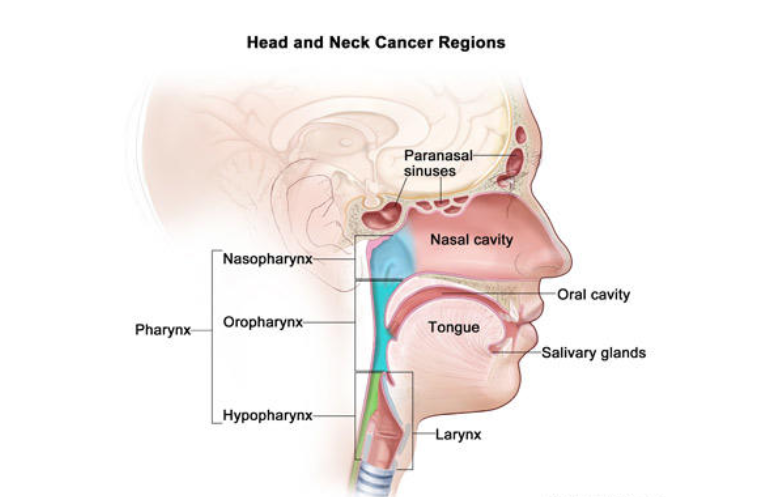
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, is a type of cancer that can develop in any part of the mouth. This includes the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard and soft palate, sinuses, and throat. If not diagnosed and treated early, oral cancer can be life-threatening. In this article, I’ll walk you through its causes, warning signs, diagnosis methods, surgical treatment options, and tips on how to take care of yourself during recovery—explained in simple terms.
What Increases the Risk of Oral Cancer?
Several factors can increase your chances of developing oral cancer. The most common is tobacco use, including smoking cigarettes, cigars, and chewing tobacco like gutka and khaini. Heavy alcohol consumption also adds to the risk, especially when combined with tobacco use. A human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, particularly HPV-16, is a leading cause of throat and mouth cancer in younger adults.
Excessive sun exposure, especially to the lips, increases the risk of lip cancer. Poor oral hygiene can contribute to long-term irritation and raise the chances of developing oral cancer. A family history of cancer, a weakened immune system, and being over 40 years old, especially in men, are also significant risk factors.
Signs and Symptoms of Oral Cancer
Early symptoms of oral cancer can look like common dental or oral issues. However, persistent signs should never be ignored. These may include:
- A sore in the mouth that doesn’t heal
- A lump or thick patch in the mouth or throat
- Difficulty chewing, swallowing, or moving your jaw or tongue
- Numbness in the tongue or other areas of the mouth
- Pain in the jaw or ear without a clear reason
- White, red, or mixed-color patches inside the mouth
- Loose teeth or dentures that suddenly don’t fit properly
- Voice changes or a persistent sore throat
If these symptoms last for more than two weeks, it is strongly advised to consult a doctor or an oral cancer specialist immediately.
How is Oral Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosing oral cancer typically involves three important steps:
Physical Examination
The doctor checks your mouth and neck for any visible lumps, ulcers, or abnormal tissue.
Biopsy
A small tissue sample from the affected area is removed and examined in a laboratory to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Imaging Tests
To assess how far the oral cancer has spread, doctors may recommend imaging tests such as:
- CT Scan (to check the size and spread of the tumor)
- MRI (to get detailed images of soft tissues)
- PET Scan (to find cancer in other parts of the body)
- X-rays (especially useful for checking the jaw or lungs)
Types of Oral Cancer Surgery
Surgery is often the first line of treatment if the mouth cancer is caught in its early stages. The type of surgery depends on the location of the tumor:
Lip Surgery
Affected portions of the upper or lower lip are removed. Reconstructive surgery is usually performed to restore appearance and function.
Tongue Surgery (Glossectomy)
Part or all of the tongue may be removed. Reconstruction helps restore speech and swallowing abilities.
Hard Palate and Upper Gum Surgery
Cancerous bone and gum tissue in the roof of the mouth are removed. Dental prostheses or bone grafts may be used for restoration.
Soft Palate Surgery
Cancer in the back of the mouth (soft palate) may require removal and reconstruction using tissue from other parts of the body.
Floor of the Mouth Surgery
Tissue beneath the tongue is removed and reconstructed to maintain speech and eating functions.
Cheek Lining Surgery (Buccal Mucosa)
Cancerous tissue inside the cheek is removed. Plastic or reconstructive surgery may be required for function and appearance.
Lower Gum and Jaw Surgery (Mandibulectomy)
When cancer affects the lower jaw, part of the jawbone may be removed and reconstructed using bone grafts.
Surgery for the Area Behind Wisdom Teeth
Due to the complexity and location, this area may require advanced surgical techniques.
Neck dissection is often done alongside these surgeries to remove nearby lymph nodes if the cancer has spread. It's important to consult the best oncologist for oral cancer to determine the most effective surgical approach.
Taking Care of Yourself After Mouth Cancer Surgery
Recovery after oral cancer surgery is just as important as the treatment. Here are key aspects of post-operative care:
Nutrition
If swallowing is difficult, you may start with a feeding tube. Gradually transition to soft foods and then a regular diet. High-protein and calorie-rich foods aid in healing.
Speech and Swallowing Therapy
A speech therapist will help you regain speaking and swallowing abilities, especially after tongue or jaw surgery.
Wound Care
Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Keep the surgical site clean and watch for signs of infection like swelling, pus, or fever.
Pain Management
Take medications as prescribed and attend follow-up appointments for pain control and healing assessment.
Dental Care
Good oral hygiene is essential. After jaw or gum surgery, regular dental check-ups are vital for long-term care.
Emotional Support
Emotional recovery is just as important. Speaking with a counselor, support group, or loved ones can help you cope better.
Lifestyle Changes
Quit tobacco and alcohol completely. Maintain a healthy lifestyle and clean oral environment to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Conclusion
Oral cancer is a serious condition, but with early diagnosis, proper treatment, and good aftercare, it is often treatable. Being aware of the symptoms, acting quickly, and following medical guidance can save lives. If you or someone you know shows any warning signs, do not delay. Consult a cancer specialist or the best oncologist for oral cancer—early action can make all the difference.
If you're seeking affordable cancer treatment in Kakinada, or looking for the best oncology treatment in the Kakinada area, Dr. K. Pradeep Bhaskar offers expertise in oral cancer diagnosis, treatment, and recovery. Don’t hesitate to reach out to an experienced oral cancer specialist in Kakinada for personalized care.
Stay informed. Stay vigilant. And let’s spread awareness about oral cancer.